📺 Watch this and other posts on YouTube or listen on Spotify, Apple Podcasts, and YouTube Music.
Intro
When long-term care insurance (LTCi) was first introduced, it wasn’t perfect. Insurers miscalculated the costs, which led to premium hikes and frustrated customers.
The mistakes were self-inflicted—like Jimmy Fallon cracking an egg on his own head. Or like Coca-Cola’s infamous launch of New Coke in 1985: a bold move that backfired fast. Here's a 30-second commercial.
The backlash was swift, and the company quickly brought back the classic formula.
In the same way, the LTCi industry stumbled early—but it didn’t stop there. Insurers learned, adapted, and came back with smarter, more reliable policies that work better for today’s consumers.
Let’s look at what went wrong and how those lessons helped shape the improvements we see today.
Post jargon
benefit: the amount LTCi pays for covered care expenses
LTC: long-term care
LTCi: long-term care insurance
MedicAID: healthcare public assistance
partnership policy: a special LTCi policy to keep assets from MedicAID
premium: the payment to maintain insurance
traditional policy: early LTC insurance referred to as "pure" LTCi
➡️ Explore all the LTC jargon
Brief history of LTCi
Below is a super abbreviated history of LTCi.

Quick timeline
- 1960s - First LTCi policies. 🏛️
- 1980s - Policies were mispriced. ❌
- 1990s - Regulations introduced. ⚖️
- 2000s - Premium increases started. Frustration. 😠
- 2010s - New hybrids launch with cash indemnity. 💡
More details
LTCi emerged in the 1960s with restrictive policies that covered only nursing home care.
By the 1980s, we had neon colors, big hair, and over 100 companies selling LTC insurance like it was the latest hit movie. But just like those perms, things didn’t age well.

Pricing problems
Beneath the surface, a bigger problem loomed. Policies were priced too low because insurers didn't know how to correctly forecast the cost of LTC.

Insurers faced several issues:
- Lack of data to predict future LTC costs
- An unexpectedly high rate of policy renewals
- Falling interest rates affected their investments
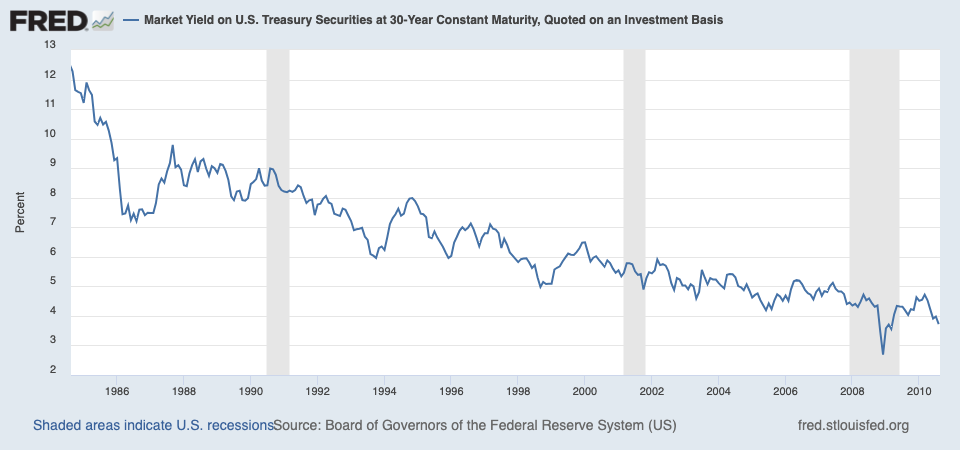
These problems resulted in insurers charging customers too little in annual premiums. Over time, this self-inflicted wound would come back to haunt them.

New regulations
Over the next decade, regulations were introduced to improve the industry.
- 1993 - NAIC introduced consumer protections, renewable policies, adding Alzheimer’s coverage, and clarified care criteria.
- 1996 - HIPPA's Section 7702(b) set a new standard for tax-qualified policies.

Premium increases
In the 2000s, insurers became aware of their mistakes and significantly raised annual premium rates on their existing policies to correct their pricing miscalculations.

Customers were stuck between a rock and a hard place. They were offered three bad choices by insurers:
- pay more every year
- agree to less benefits
- cancel their policies

Many insurers stopped selling LTCi (only 10-15 remain), and new regulations followed:
- 2002 - NAIC introduced "Rate Stability" rules to limit premium increases.
- 2005 - The Deficit Reduction Act created long-term care partnership plans.
- 2010s - Technology improved underwriting and pricing models.
Reputational damage
Understandably, the history of underpricing policies and the resulting rate hikes caused huge customer frustration.

The mistakes also caused reputational damage to the LTCi industry. Check out this report from the New York Times and KFF about the problems of many old policies:
Or, if you're a visual learner, check out this 4-minute video from the Wall Street Journal covering the same issues:
Improved long-term care insurance
If you only read the headlines, you wouldn't consider insurance as a good option in your long-term care planning. But you might miss the bigger story.
Long-term care insurance policies have improved. To stick with our Coca-Cola example, the bad-tasting soda is no longer being sold.

If you purchase a new traditional policy, it typically includes:
- new regulations for consumer protection
- better pricing to prevent big price hikes
- improved tax benefits
- partnership plan benefits (keep your assets from MedicAID)
While some traditional policies can technically can raise rates in the future, it’s highly unlikely. These policies are conservatively priced, and carriers have decades of data to help them set stable premiums.
Even better, a new type of policy was created, hybrids, that fixes other issues of traditional plans, including premiums that can never go up.

Wrap up
Ask friends and family about their experiences with long-term care insurance, and you'll likely hear one of two stories.
- Good - "My mother had long-term care insurance, and it was a godsend when she moved into an assisted living facility."
- Bad - "I purchased long-term care insurance twenty years ago, and they raised my annual premiums by 100%. I'm so angry."
To put it in perspective, most people won’t use their LTC benefits until 25+ years after purchasing a policy. Since hybrid policies with cash indemnity only became available in the late 2010s, it will be decades before we hear their success stories.
Don’t want to relive the mistakes of the past? Dive into the new world of LTC insurance—no bad-tasting sodas here, just better coverage for you and your family.